Researchers at the Facultad de Informatica collaborate on the Blue Brain Project
Researchers at the Universidad Politecnica de Madrid's Facultad de Informatica have developed a high-quality cerebral cortex image rendering engine. The rendered images are used to generate 3D videos and movies to promote the scientific understanding of the Blue Brain project.
The research was conducted as a final-year project by Omar Agudo Silva and was supervised by José María Peña and Juan Hernando Vieites. They are members of the Facultad de Informatica's Department of Computer Systems Architecture and Technology.
The international Blue Brain Project (BBP) is the first global attempt to reverse engineer the mammalian brain. The project aims to use computer simulations to study brain function and dysfunction.
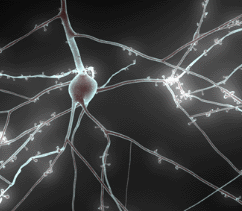
The research helps BBP scientists to generate high-quality 3D images, videos and movies to communicate BBP results to the scientific community and general public. Therefore, they can focus on the message they want to convey rather than wrestling with the technicalities of video production.
The proposal was to build a rendering engine. A rendering engine is a specialized software to generate 3D scene images using graphical techniques such as ray tracing. The developed engine is capable of producing high-quality images of BBP neuron models and simulations.
Movie animation techniques
The engine employs the rendering technique of ray tracing. Ray tracing is widely used in movie animation and is capable of generating high-quality images. The idea behind this algorithm is to imitate how rays of light interact with surfaces to simulate a wide variety of optical phenomena, such as reflection, refraction or dispersion.
The technique is capable of producing extremely realistic images, albeit at a high computational cost. On this ground, this research also focused on minimizing the consumption of memory and time resources to generate images from the neuron models and simulations.
The rendering engine employs existing ray tracing image generation software, which is integrated into the BBP software architecture. Users have a simple mechanism for setting up the engine, offering a choice of different rendering options. One of the options is able to generate stereo image pairs, that is, images that can be used to produce stereoscopic 3D films.
Additionally, a new technique has been designed and implemented to display simulation information by assigning colour and transparency to the neurons depending on the magnitude represented. This is an important aspect to reduce resource consumption.